Nursing Diagnosis Basics Nurse Key

Nursing Diagnosis Blank Nursing Care Plan Templates 5 regarding Nursing Care Plan Templates
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a disease in which a waxy substance called plaque builds up inside the coronary arteries. These arteries supply oxygen‐rich blood to your heart muscle. When plaque builds up in the arteries, the condition is called atherosclerosis (ATH‐er‐o‐skler‐O‐sis).

SOLUTION Nursing Diagnosis Fn Studypool
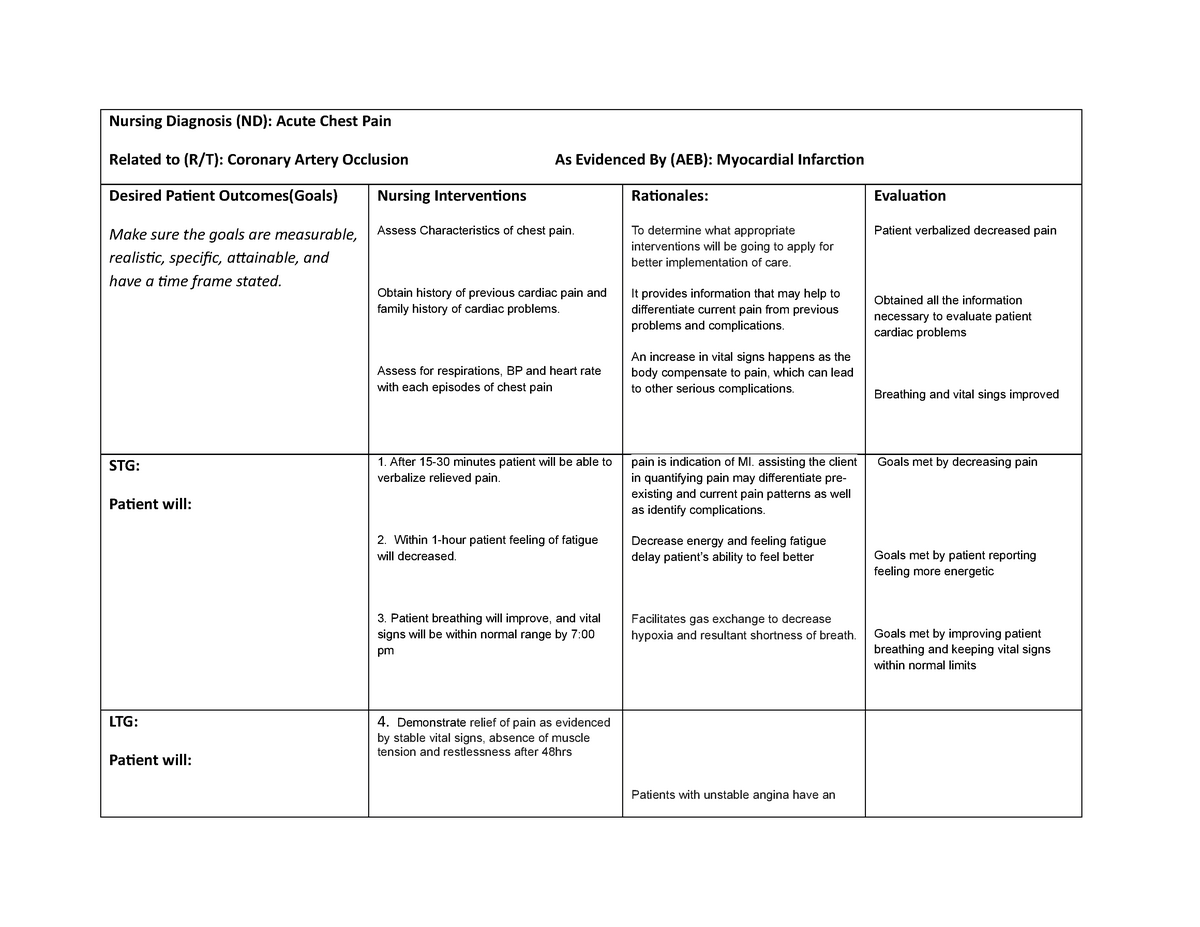
Rationale: Angina is a symptom of progressive coronary artery disease that should be monitored and may require occasional adjustment of treatment regimen. Nursing Diagnosis: Anxiety. May be related to. Situational crises; Threat to self-concept (altered image/abilities) Underlying pathophysiological response

What is a Nursing Concept Map? Examples & Templates Nurses News Hubb
Evaluation Algorithm for Patients with suspected ACS at Intermediate Risk with No Known CAD, Figure 10. Evaluation Algorithm for Patients with suspected ACS at Intermediate Risk with Known CAD, Table 9. Differential Diagnosis of Noncardiac Chest Pain Accompanying Symptoms. Chest pain is the dominant and most frequent symptom for both men and
Coronary Artery Disease Cad Nursing Diagnosis Care Plan Nursestudy Net PELAJARAN
Coronary artery disease is a condition that puts you at risk for heart attack and other forms of heart disease. In people who have coronary artery disease, the arteries that supply blood to the heart get clogged with fatty deposits ( figure 1 ). Other names for this disease are "coronary heart disease" or just "heart disease."

Nursing Diagnosis Basics Nurse Key
1. Managing Acute Chest Pain and Discomfort 2. Administering Medications and Providing Pharmacologic Interventions 3. Decreasing Oxygen Demand and Managing Decreased Cardiac Output 4. Monitoring and Preventing Potential Myocardial Complications 5. Providing Emotional Support and Reducing Anxiety 6.

Copd Nursing Care Plan Sample Best Image Nanda Nursing Diagnosis For Vrogue
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a duration used the describe conditions that affect this arteries that provide nutrients, blood, and sufficient at this heart. Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a terminology used to describe conditions that influencing the arteries that provide nutrients, blood, and amount for to heart.

Texas A&M University, KingsvilleNURS MISC391320168TestBankforFundamentalsofNursin
This procedure is done to open clogged heart arteries. It may also be called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). The heart doctor (cardiologist) guides a thin, flexible tube (catheter) to the narrowed part of the heart artery. A tiny balloon is inflated to help widen the blocked artery and improve blood flow.

Nursing diagnosis, implenenting, and evaluation Bingo Cards WordMint
Diagnosis, management and nursing care in acute coronary syndrome | Nursing Times. Abstract Acute coronary syndrome refers to a range of potentially life-threatening conditions that affect the coronary artery blood supply to the heart,

Nursing Diagnosis Guide for 2023 Complete List & Tutorial Nurseslabs The Ultimate Guide to
Coronary artery disease is very common. Over 18 million adults in the U.S. have coronary artery disease. That's roughly the combined populations of New York City, Los Angeles, Chicago and Houston. In 2021, coronary artery disease killed 375,500 people in the U.S. Coronary artery disease is the leading cause of death in the U.S. and around the.

NURSE UN 311 A&E I Comprehensive Test bank Latest Updated Already Passed in 2023 Test bank
Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG), often known as heart bypass surgery, is a medical procedure used to enhance blood flow to the heart. This procedure is beneficial in managing atherosclerosis, a form of coronary artery disease (CAD).
Nursing Care Plan Risk For Infection Table 5 From Nursing Diagnoses Vrogue
Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goals Nursing Interventions and Actions 1. Initiating Interventions for Decrease in Cardiac Output 2. Monitoring Diagnostic Procedures and Laboratory Studies 3. Administering Medication and Providing Pharmacological Interventions 4. Maintaining or Improving Respiratory Function 5.

10 Nursing Assessment Mnemonics You Should Know Now
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a condition that affects the coronary arteries, which are the blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart. When these arteries become narrowed or blocked, it can cause chest pain (angina) or even a heart attack.

Pin on nursing life
A total of 13 nursing diagnoses were evaluated from the medical records of 50 outpatients with the following validation agreements among the specialists: Ineffective health management (100%), Noncompliance (100%), Sedentary lifestyle (100%), Activity intolerance (100%), Decreased cardiac output (88%), Risk of decreased cardiac tissue perfusion (.
nursing diagnosis care plan pediatrics HEA 145 Studocu
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is one of the leading causes of death. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a non-surgical, invasive procedure with the goal of relieving the narrowing or occlusion of the coronary artery and improve blood supply to the ischemic tissue. This is usually achieved by different methods, the most common being ballooning the narrow segment or deploying a stent to.

SOLUTION Nursing diagnosis Studypool
Coronary artery disease is a condition in which there is an inadequate supply of blood and oxygen to the myocardium. It results from occlusion of the coronary arteries and results in a demand-supply mismatch of oxygen. It typically involves the formation of plaques in the lumen of coronary arteries that impede blood flow. It is the major cause of death in the US and worldwide. At the beginning.

Nursing Exam, Nursing Diagnosis, Nursing Notes, Past Exam Papers, Past Exams, Testing Techniques
Nursing Care Plan for Acute Coronary Syndrome 2. Risk for Decreased Cardiac Output. Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for Decreased Cardiac Output related to Changes in Heart Rate and Rhythm. Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to maintain stable cardiac output as evidenced by a normal heart rate without dysrhythmias.